SWIFT Customer Security Program (CSP)
Launched in 2016, the Swift Customer Security Programme (CSP) aims to enhance cyber-security across its network, mitigating the risk of cyber-attacks and minimizing the impact of fraudulent transactions. Through continuous evolution to address the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, the CSP mandates a set of security controls for Swift users to implement, ensuring a secure financial ecosystem. These controls, part of the Customer Security Controls Framework (CSCF), include both mandatory and advisory measures, informed by industry standards and feedback, to protect against and respond to cyber threats effectively.
Swift’s CSP encourages industry-wide collaboration, requiring users to annually attest to their compliance with these security controls through the KYC Security Attestation application. This process promotes transparency and peer-driven security enhancements across the network. With the dynamic nature of cyber threats, Swift continuously updates the CSCF, advising users to consult the latest version for current security practices, thereby supporting the ongoing effort to fortify the financial sector’s defenses against cyber risks.
SWIFT CSP MAIN BUILDING BLOCKS
- Formal set of security controls (mandatory and advisory)
- Once per year, every BIC needs to verify compliance with all mandatory (at least) controls and attest in an online tool (KYC-SA)
- Controls reviewed annually by Swift and with the community
- Further supporting the attestation with an independent assessment
- Objective is to verify the effective implementation of the controls
- Assessors may be internal and/or external
- Assessment details are also logged in KYC-SA
SWIFT CUSTOMER SECURITY FRAMEWORK
The security controls are based on three overarching framework objectives, supported by seven security principles. Objectives are the highest level structure for security within the user’s environment. The associated principles elaborate on the highest priority focus areas within each objective.
Swift’s CSP encourages industry-wide collaboration, requiring users to annually attest to their compliance with these security controls through the KYC Security Attestation application. This process promotes transparency and peer-driven security enhancements across the network. With the dynamic nature of cyber threats, Swift continuously updates the CSCF, advising users to consult the latest version for current security practices, thereby supporting the ongoing effort to fortify the financial sector’s defenses against cyber risks.
Objectives
Principles
Controls
Secure Your Environment
- Restrict Internet access & Segregate critical systems from general IT environment
- Reduce attack surface and vulnerabilities
- Physically secure the environment
Know and Limit Access
4. Prevent compromise of credentials
5. Manage identities and segregate privileges
Detect and Respond
6. Detect anomalous activity to system or transaction record
7. Plan for incident response and information sharing
SCOPE OF SECURITY CONTROLS
The scope of security controls in CSCF encompasses a defined set of components in the user’s environment.
In-Scope Components:
- User’s SWIFT Infrastructure
- Operators/Operator PCs
- Data Exchange Layer
- Middleware Server
- File Transfer Server
Out of Scope Components:
- User back office
- General Enterprise IT Environment
- Network/Internet Connections
- Test and Development Systems
Co-hosting Components:
Non-SWIFT related systems hosted in the secure zone must be protected to an equivalent level of security and trust by applying controls applicable to the Swift-related components.
Sharing/Reusing Credentials:
Services such as transaction queries, pre-validation, and screening are typically out of scope unless they share credentials and entitlements with business transactions, which then brings those systems into scope.
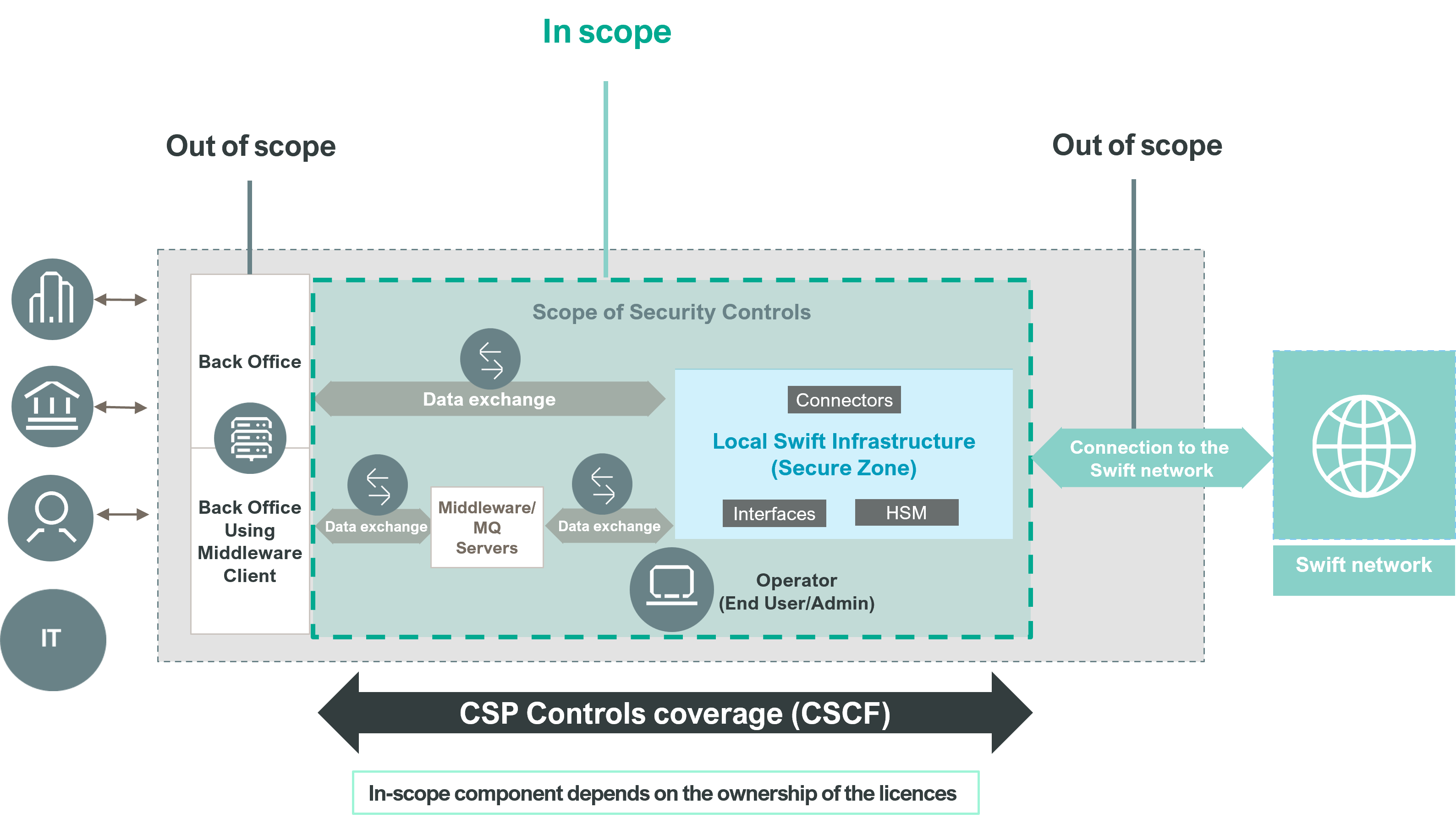
SWIFT Architecture Types
Users must select from five reference architecture types that best reflect their deployment to identify in-scope components, using a CSP decision tree for guidance. The choice of architecture, which should be the most encompassing, affects the applicability of certain security controls. These architectures differ primarily based on the ownership of components or licenses.
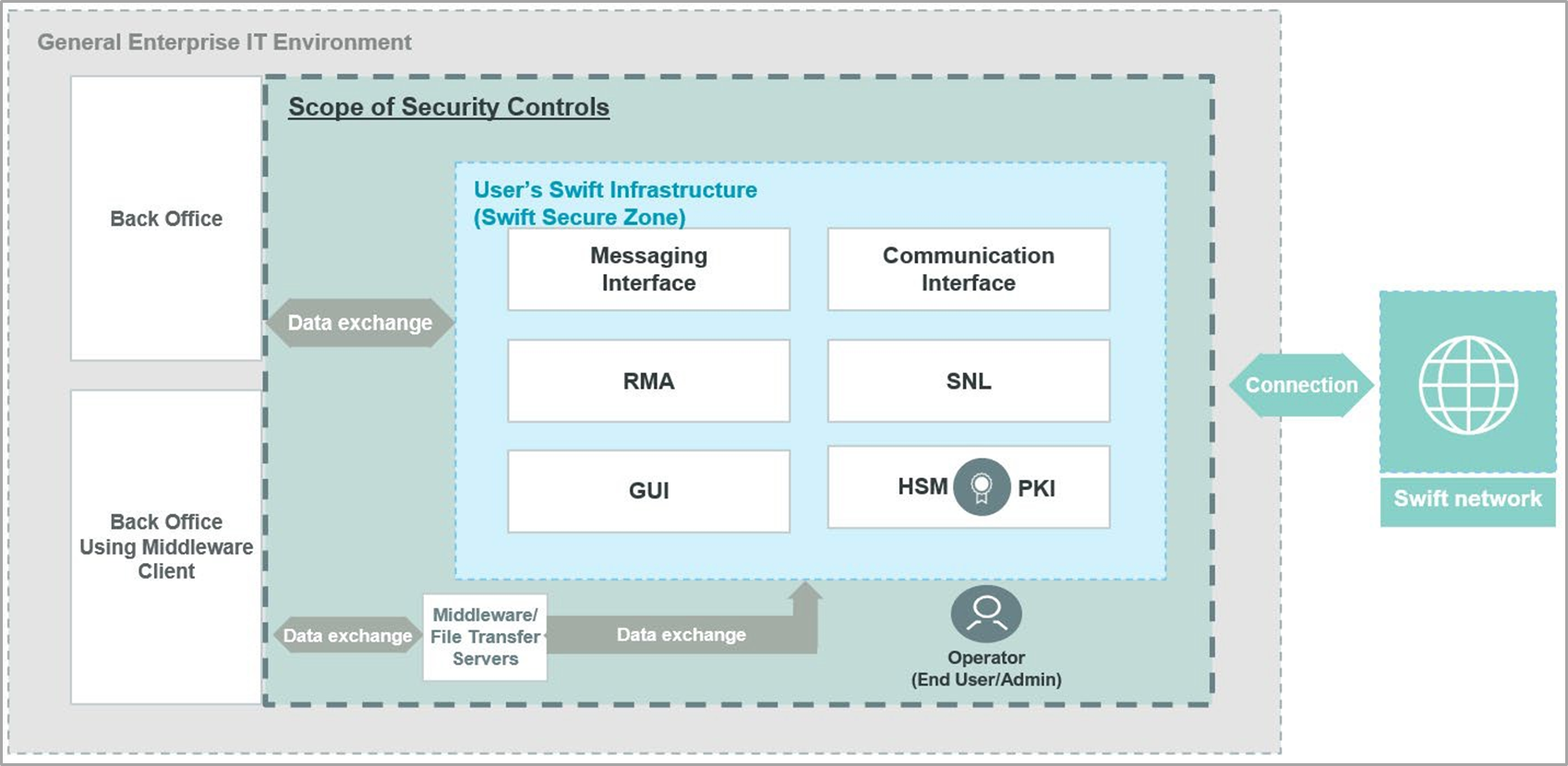
Architecture Type A1 (Communication Interface)
Architecture A1 is defined by user ownership of the communication interface, often including the messaging interface as well. Architecture A1 also applies to scenarios where the user owns only the communication interface. This category encompasses hosted solutions where the user owns a communication interface license operated either on behalf of others or by a third party for the user’s personal use, inside or outside their environment, such as an Alliance Gateway Instant connected to a back-office system without a Messaging Interface.
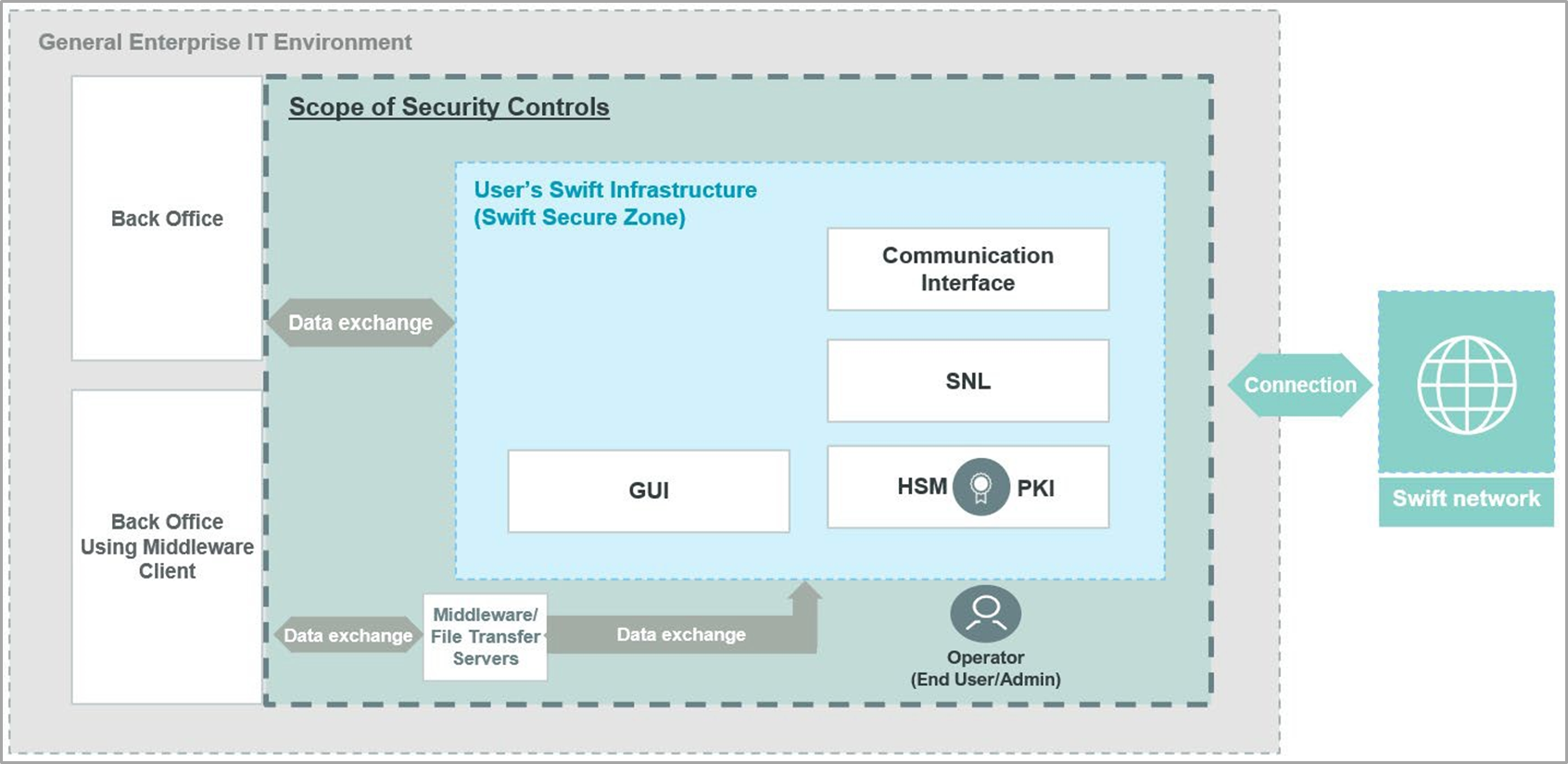
Architecture Type A2 (Messaging Interface Only)
In Architecture A2, users own the messaging interface while the communication interface is managed by a service provider, such as a service bureau or Swift. This architecture also covers instances where the messaging interface license, owned by the user, is hosted or operated by a third party or service provider, acting as an outsourcing agent.
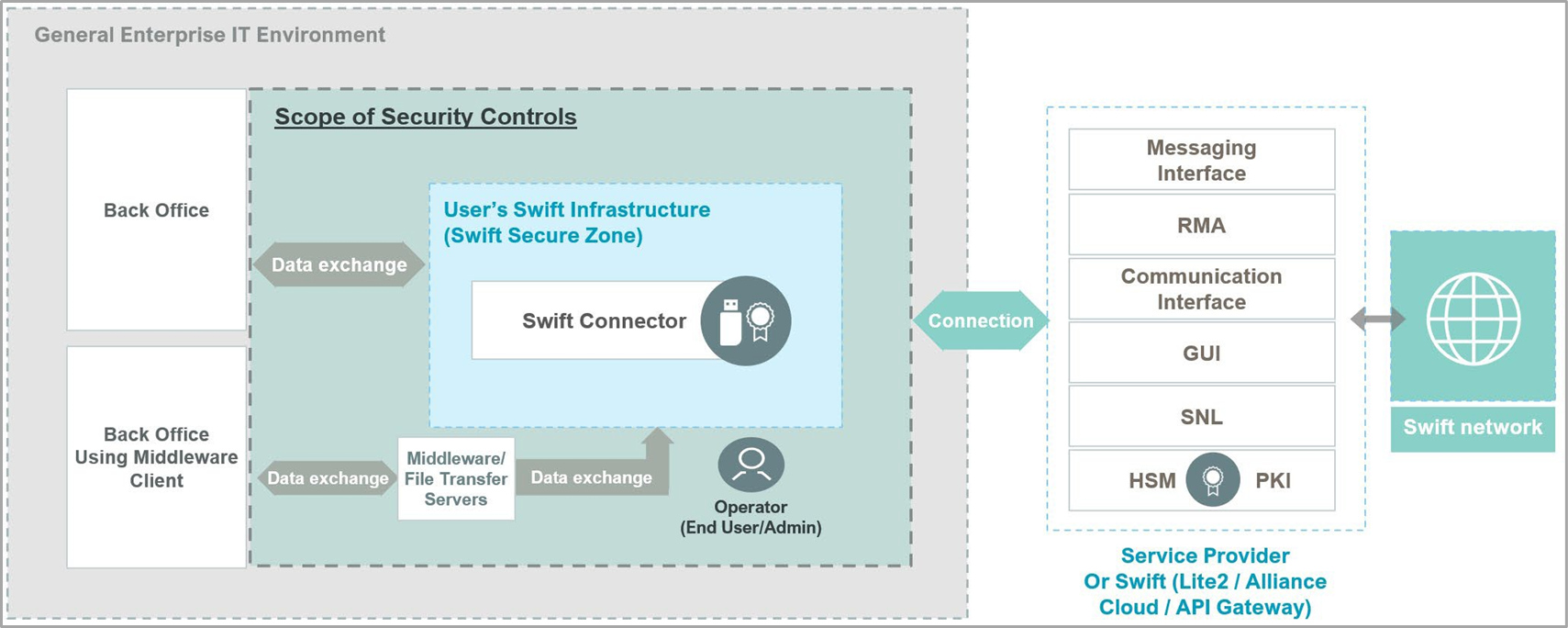
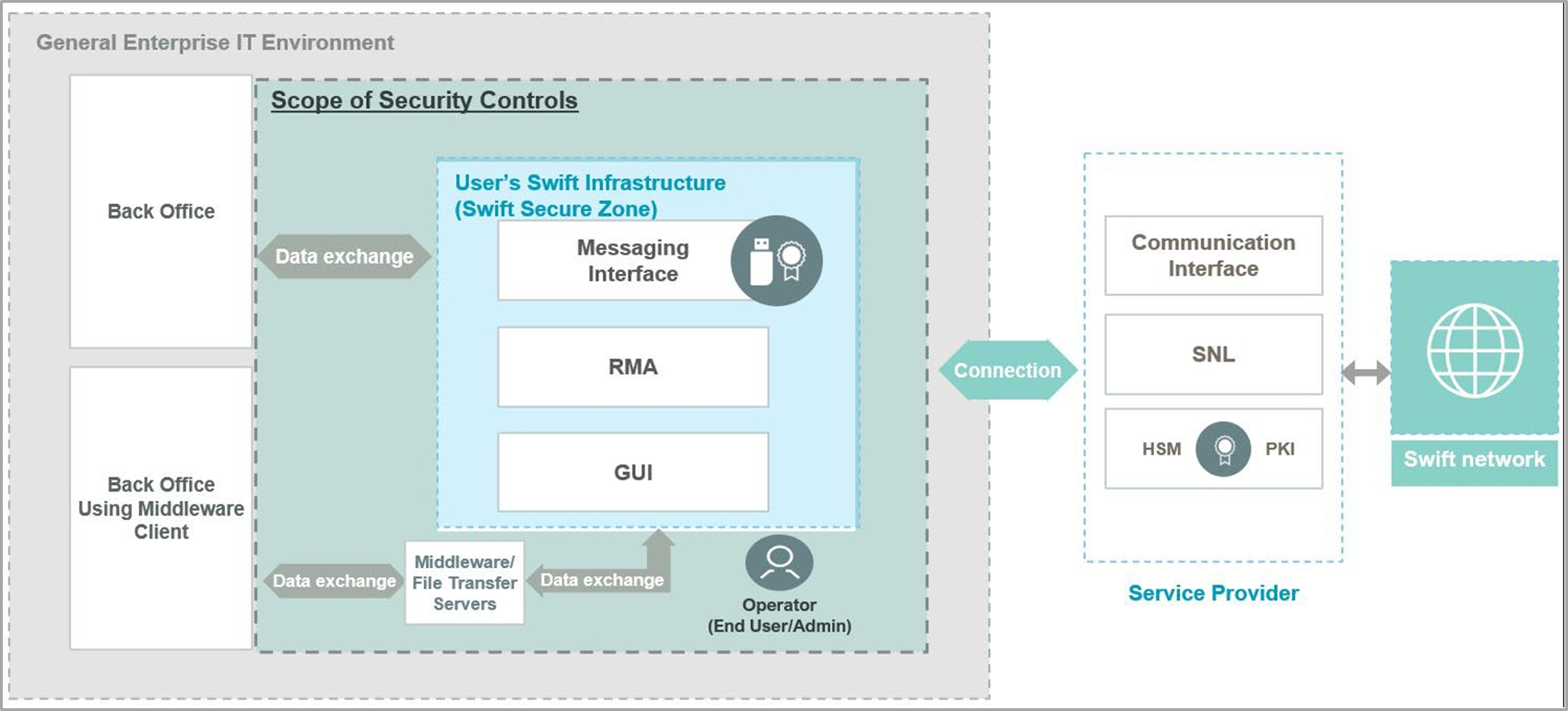
Architecture Type A3 (SWIFT Connector)
A Swift connector is employed within the user’s environment to enable application-to-application communication with a service provider’s interface (like a service bureau or a Group Hub) or Swift services (e.g., Alliance Cloud or Alliance Lite2), without owning any messaging or communication interface.
This setup may also incorporate a GUI solution for user-to-application interaction, requiring the implementation of additional controls related to the GUI. Furthermore, this architecture encompasses scenarios where the user’s Swift connector is hosted or managed by a third party or service provider, which should be regarded as an outsourcing agent in these instances.
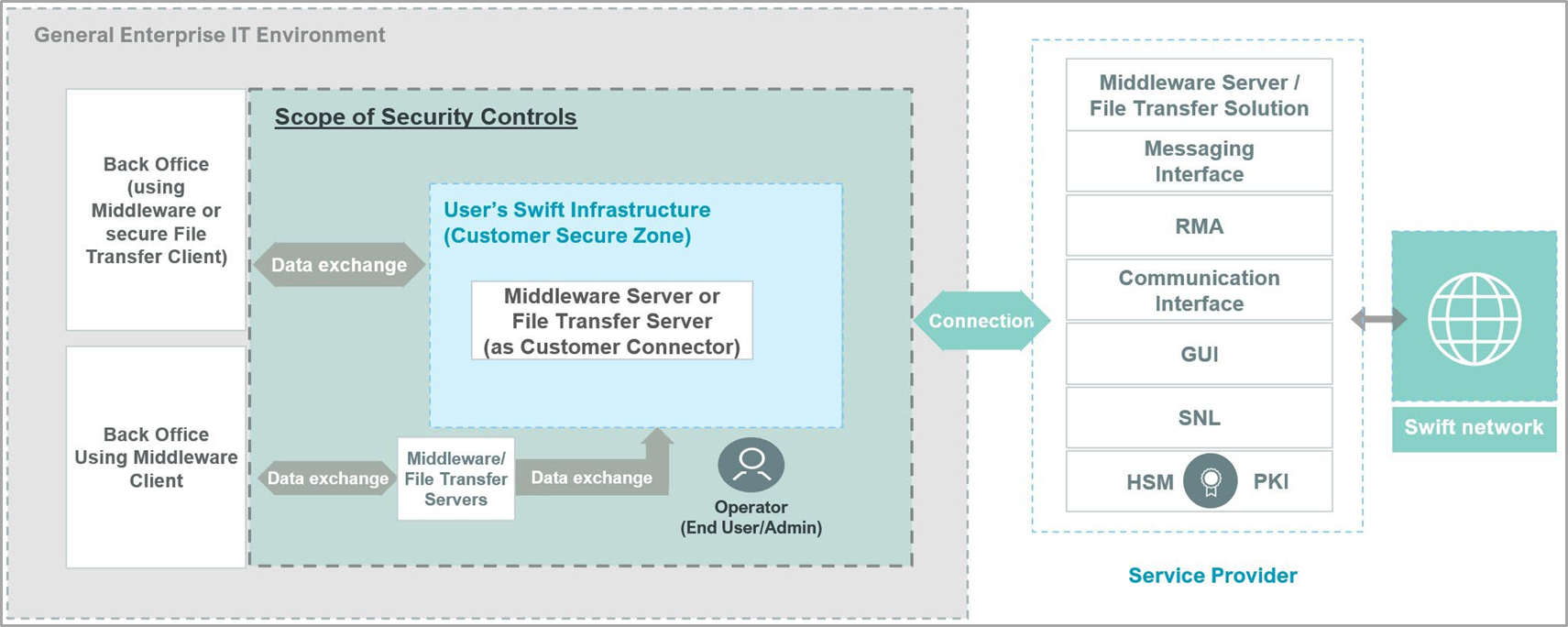
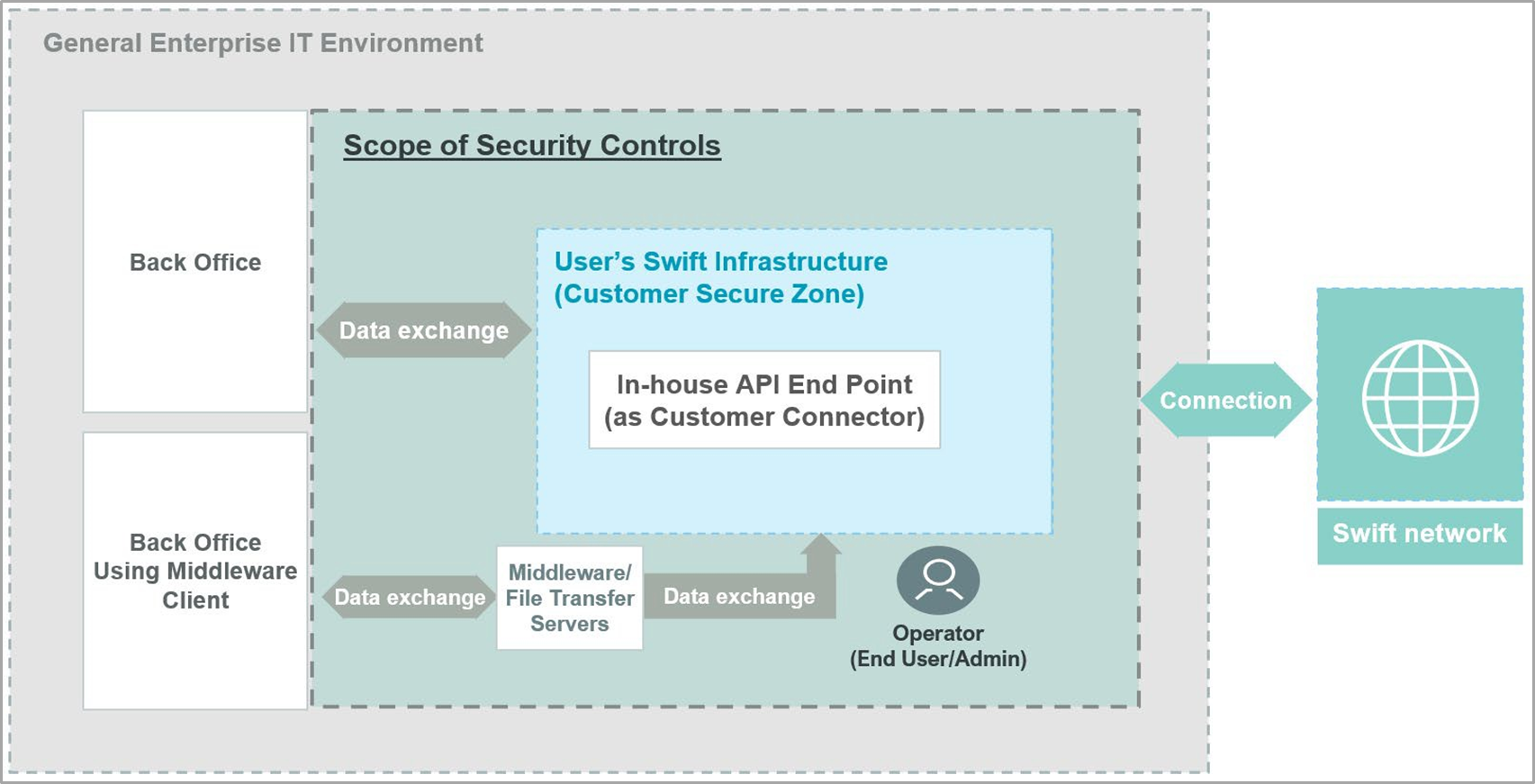
Architecture Type A4 (Customer Connector)
Architecture A4, known as the Customer Connector, applies to users without a direct Swift presence, utilizing a server within their environment (e.g., a file transfer solution or middleware server) to establish external application-to-application connections with Swift-related applications or solutions provided by a service bureau, Business Connect, Lite2 Business Application provider, or Group Hub. This architecture also covers cases where the customer connector is hosted or operated by a third party or service provider, acting as an outsourcing agent.
The framework includes using file transfer or middleware servers for connections not through WAN or VLAN, without a Swift connector, and applies to setups where customer connectors use Swift APIs for direct transactions with Swift services. Additionally, it may involve GUI solutions requiring GUI-specific controls. Like other architectures, while back-office systems generating transactions usually fall outside CSP/CSCF scope, implementing security controls based on industry frameworks and CSCF principles is advised to mitigate broader transaction chain risks.
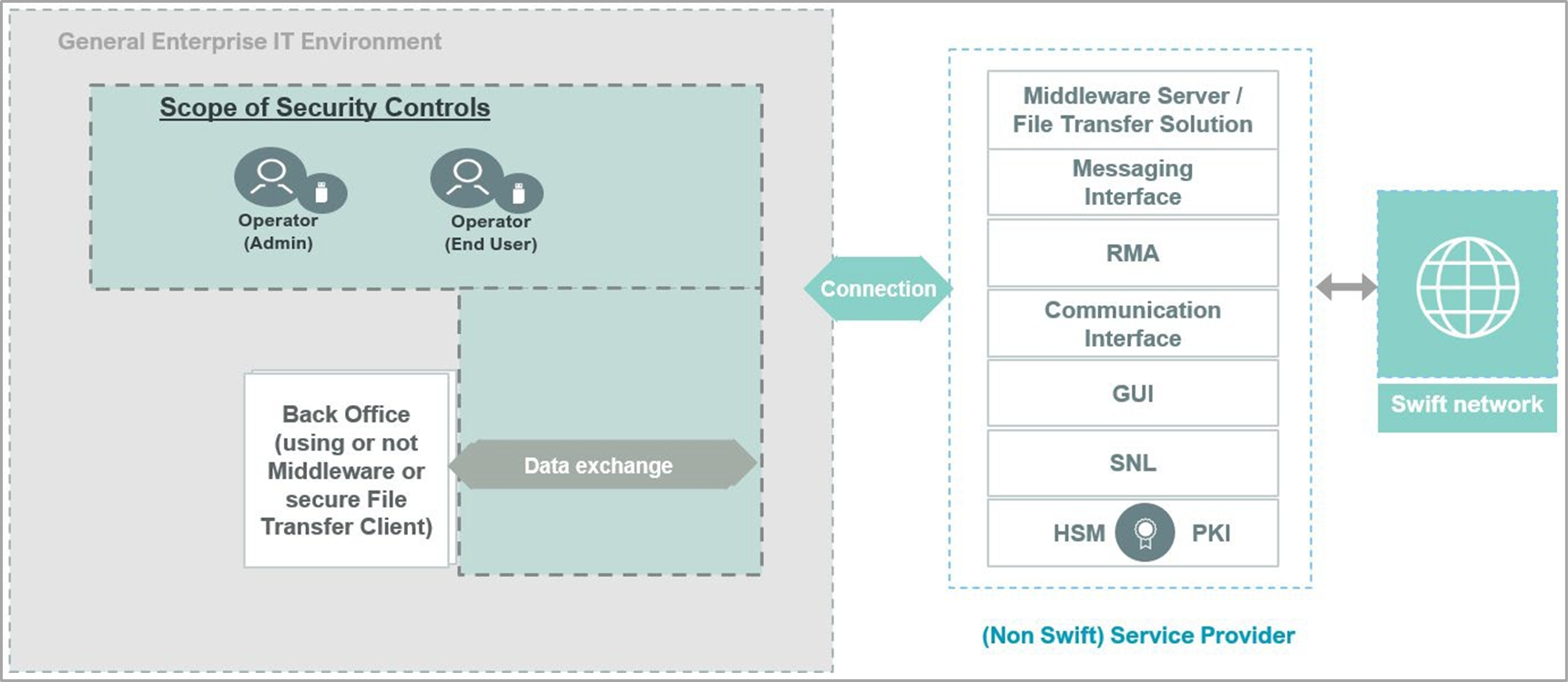
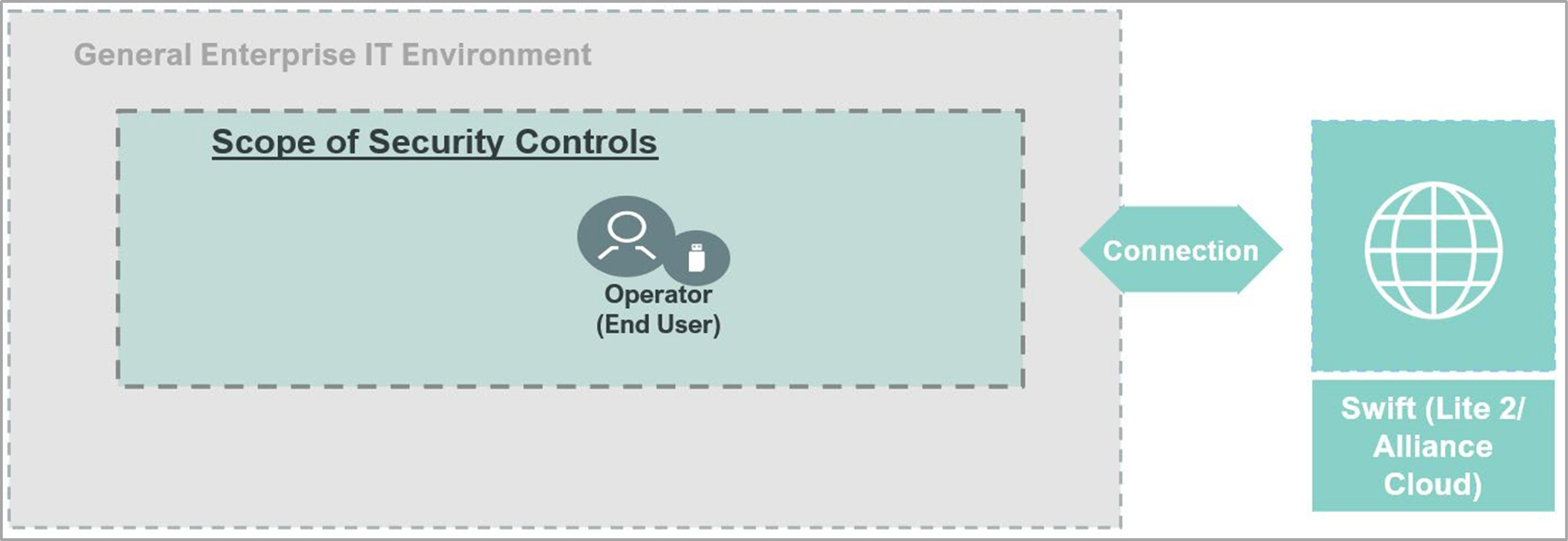
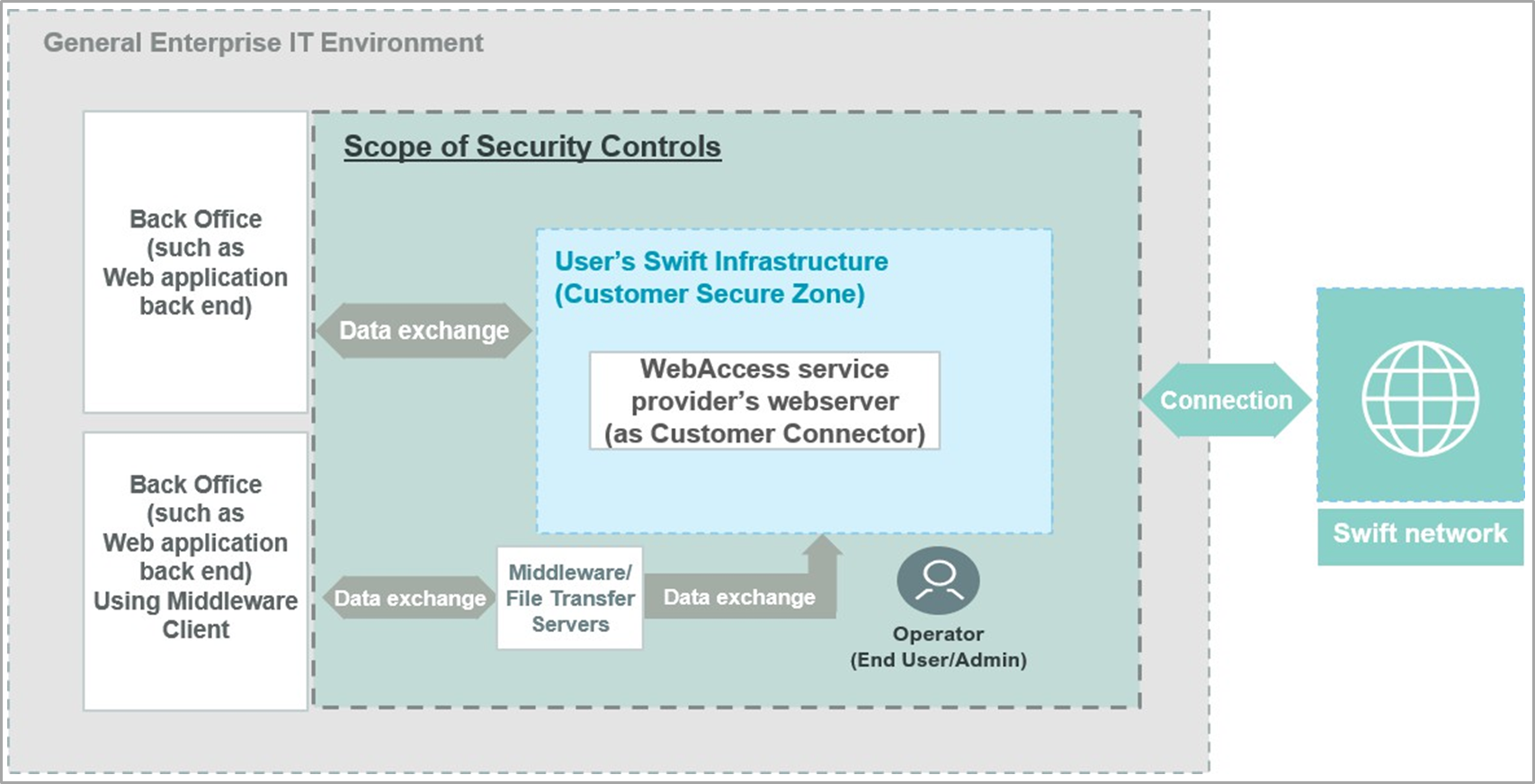
Architecture Type B (GUI or Middleware Client)
Architecture B outlines scenarios where users engage with Swift services without any Swift-specific infrastructure in their local environment. This architecture encompasses two main setups: users accessing Swift messaging services via a GUI application provided by a service provider, and back-office applications of users communicating directly with the service provider using various clients (e.g., MQ, Kafka, Solace) or secure file transfer clients, without directly connecting to Swift’s specific messaging services. Devices used in these interactions are treated as general-purpose and require adequate protection.
INDEPENDENT ASSESSMENT FRAMEWORK
Swift mandates the independent assessment of all mandatory controls for attestations, as supported by Swift’s Board and Oversight, to ensure integrity, consistency, and accuracy. Independent assessors must verify that these controls achieve their objectives, cover all in-scope components, and address risk drivers. While implementing advisory controls is advised but optional, they also require independent assessment if included in the attestation. The outcomes, reflecting compliance levels, must be documented annually in the KYC Security Attestation (KYC-SA) application, accompanied by assessment reports and confirmation letters.
Asessment Types
There are three types of assessment under the CSP
Self-Assessment:
Self-Assessments, conducted by risk-managing functions without independent review, are labeled as ‘not compliant’ in the KYC Security Attestation (KYC-SA) application. This status is immediately visible to counterparts and flagged in the Know-Your-Customer for Supervisors (KYS) app for supervised users, with bi-annual reports available. Choosing a self-assessment is a strategic decision for Swift users, fully aware of its non-compliance implications.
Community Standard Assessment:
Swift recognizes two types of independent assessments: External, carried out by an independent organization, and Internal, conducted by the user’s own independent department (e.g., compliance, risk management, internal audit), separate from the attesting first line-of-defense. Assessors, whether internal or external, must have relevant cyber-security control assessment experience and qualifications.
SWIFT-Mandated External Assessment:
Swift may require specific BICs to undergo external assessments to verify their KYC-SA attestations’ accuracy, as stated in the Customer Security Controls Policy (CSCP) under “Quality assurance.” This process involves an independent external assessor confirming the user’s adherence to the applicable controls. Compliance with such mandated external assessments is crucial for maintaining robust security within the Swift network. Failure to complete these assessments constitutes a violation of the CSCP, and Swift may report non-compliance to the appropriate supervisory bodies and/or the non-compliant BICs’ counterparties.
Choosing Assessment Provider
SWIFT CSP Assessors Directory | Swift
Our Assessment Process
Objective: Prepare for the assessment by understanding the Swift user's environment and objectives.
Activities: Collect architecture documentation, use CSCF and decision tree for CSP architecture type, derive applicable CSP controls, and conduct workshops for scope definition.
Inputs: Architecture documentation, key processes, and Swift CSP documentation.
Outputs: Assessment scope, agreed schedule, assigned resources.
Objective: Swift users prepare and share all necessary documents identified in the high-level test plan guidelines.
Activities: Swift users gather and provide documentation and evidence crucial for assessing compliance with CSP controls.
Inputs: High-Level Test Plan guidelines, document list.
Outputs: Collected documents and evidence for assessment.
Objective: Evaluate the shared documents to check compliance and identify further information needs.
Activities: Assessors review documents, categorize them based on relevance to CSP controls, and prepare for interviews.
Inputs: Shared documents and evidence.
Outputs: Identified gaps, additional interview requirements.
Objective: Conduct in-depth discussions to assess compliance and gather more information.
Activities: Carry out audit sessions with Swift users to demonstrate, explain, and provide additional insights into the implementation of controls.
Inputs: Prepared questions, documented review insights.
Outputs: Detailed findings from discussions, additional evidence.
Objective: Create necessary reports and confirmation letters as directed by the Swift CSP program.
Activities: Compile assessment findings into reports, fill in completion letters, and support the drafting of the KYC-SA attestation.
Inputs: Assessment findings, test results, interview notes.
Outputs: CSP Assessment Report, Independent Assessment Report, Completion Letter, KYC-SA attestation.
Elevate Your Cybersecurity with Swift CSP Assessment Services
some of Our swift cSP References













